全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
【Capacity】0.5-3 TPH
【Feeding Size】 <30mm
【Discharge Size】 0.074-0.6mm
【Procesible Material】 Gold, iron, molybdenum, lead, zinc, antimony, etc.
【Advantages】Pan Mill is now the best and most economical replacement for small or medium-scale milling machines, such as ball mills. It is widely used in small and medium mineral processing plants in African countries like Sudan.
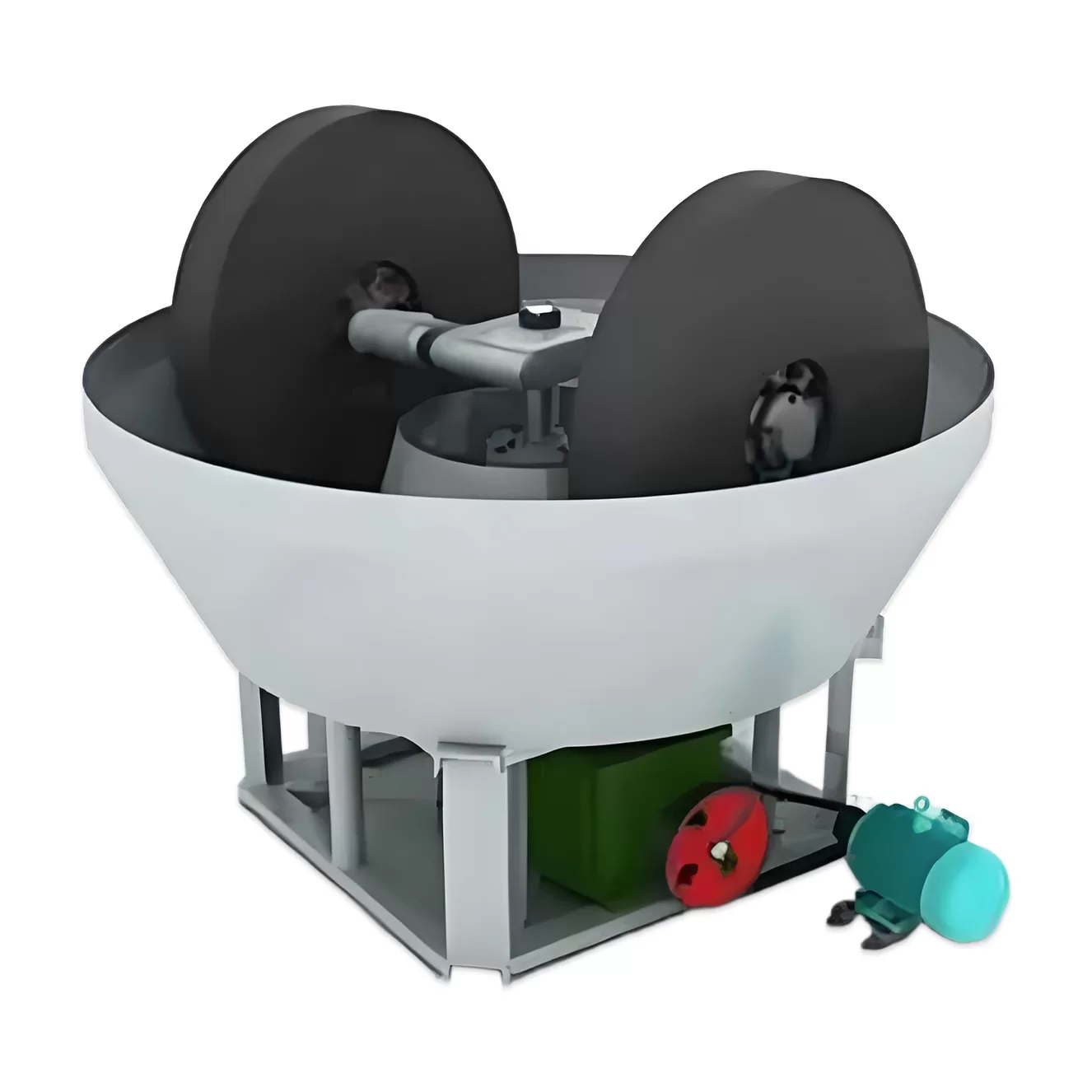
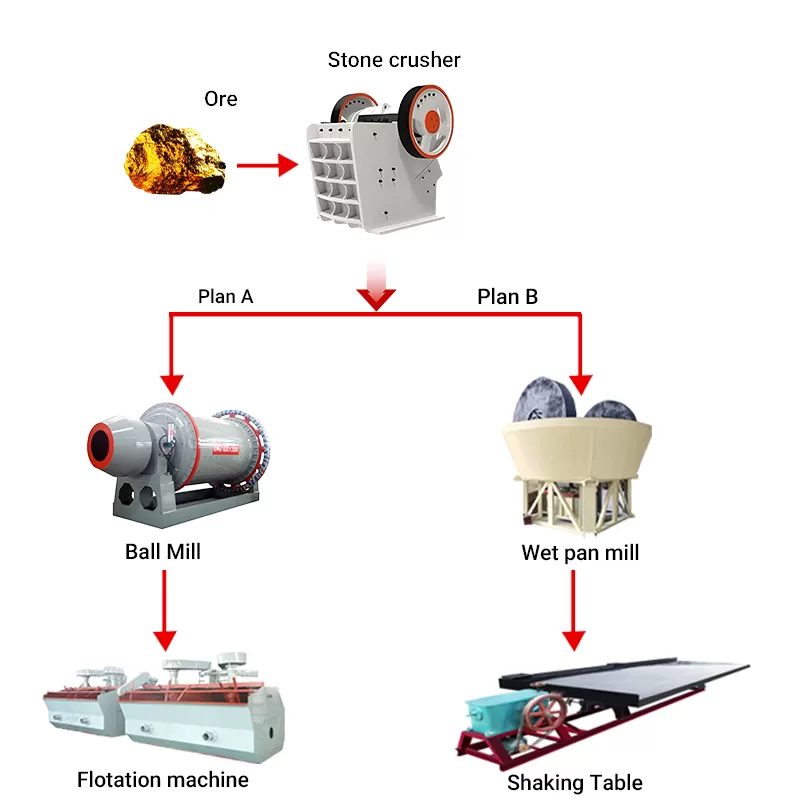
Wet mill, also known as wet mill, is a kind of grinding equipment developed on the basis of traditional stone mill. It is mainly used for grinding various metal minerals (such as gold, silver, lead, zinc, molybdenum, iron, copper, etc.) and non-metallic minerals, further grinding the crushed materials, so that the useful minerals and chalcopyrite minerals are dissociated, and conditions are created for the subsequent sorting operations (such as flotation, re-election, magnetic separation, etc.). Wet mill is especially suitable for small and medium-sized mineral processing plant.


The wet pan mill mainly consists of a power unit (motor, reducer), frame, water basin, grinding wheel, and grinding pan, adopting wheel-driven grinding.
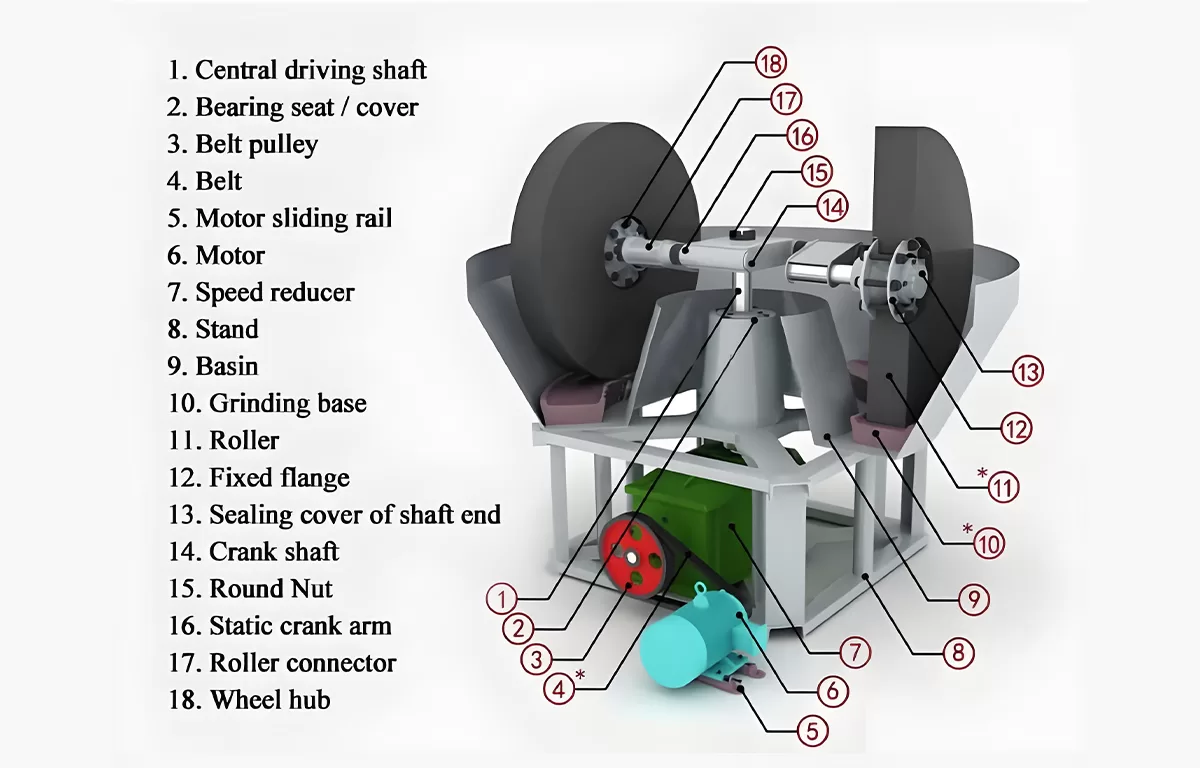
The motor drives the vertical main shaft through a reducer.
The vertical main shaft transmits torque to the horizontal shaft above.
Pull rods at both ends of the horizontal shaft drive the grinding wheels.
The grinding wheels both revolve around the vertical main shaft (revolution) and rotate around their own axes (rotation). This dual motion creates crushing and kneading effects on materials.
The grinding pan is fixed to the frame and remains stationary.
How are minerals crushed and ground?
In summary, the wet pan mill combines the grinding wheels’ dual motion with a fixed pan to pulverize minerals through pressure and friction, offering simple structure, easy operation, and low investment costs.
Minerals and water are fed into the water basin.
The grinding wheels apply pressure through their weight during revolution and rotation.
Intense friction between grinding wheels and pan subjects minerals to repeated compression, kneading, and grinding.
Scrapers on the grinding pan continuously push materials under the wheels for uniform processing.
Properly ground minerals discharge with water flow, completing the grinding process.
| Model | 1600 | 1400 | 1300 | 1200 | 1100 | 1000 | 900 |
| Dia.of grinding wheel (mm) | 1600(+-)10 | 1400(+-)10 | 1300(+-)10 | 1200(+-)10 | 1100(+-)10 | 1000(+-)10 | 900(+-)10 |
| Thickness of grinding wheel(mm) | 400(+-)20 | 250(+-)20 | 250(+-)20 | 200(+-)20 | 200(+-)20 | 200(+-)20 | 160(+-)20 |
| Dia.of grinding pan (mm) | 2100(+-)30 | 2000(+-)30 | 2000(+-)30 | 1800(+-)20 | 1800(+-)20 | 1800(+-)20 | 1700(+-)20 |
| Thickness of grinding pan (mm) | 200(+-)10 | 170(+-)10 | 150(+-)10 | 90(+-)10 | 90(+-)10 | 90(+-)10 | 80(+-)10 |
| Width of grinding pan (mm) | 360 | 360 | 360 | 230-250 | 230-250 | 230-250 | 170-220 |
| Power (kw) | 25 | 18.5 | 15 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 3 |
| Rotary speed (r/min) | For extract gold: 10-13 other: 18-22 | ||||||
| Input size (mm) | < 25 | ||||||
| Capacity (t/day) | Gold 20 | Gold 20 | Gold 15 | Gold 10 | Gold 8 | Gold 5 | Gold 3 |
| Weight(t) | 14.5 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 5 | 4.5 | 3 |
Mineral properties:
Production scale:
Economic factors:



Answer: Key factors influencing separation include the table’s motion (stroke and frequency), water volume and slope, feed rate and concentration, and the feed material’s particle size and shape. Proper adjustment of these factors is critical for efficient separation. The table’s longitudinal and transverse slopes must be precisely controlled. The feed concentration should also be appropriate, typically 20-30% for coarse minerals and 15-25% for fine minerals.
Answer: Operation involves observing the bed surface and adjusting the slope, water flow, and feed rate. Regular maintenance includes checking for loose parts, lubricating moving components, inspecting for wear, and cleaning the table surface. Preventative maintenance should be performed regularly, with intervals ranging from every month to once a year.
Answer: Common issues can include table shaking or choppy cuts, uneven material distribution, or poor separation. Troubleshooting may involve checking for loose bolts, damaged springs, or misalignment, adjusting belt tension, inspecting electrical components, and ensuring proper lubrication. If there’s unusual noise, identify the source and eliminate the problem.
Answer:
Advantages: Shaking tables offer high enrichment ratios, are relatively simple to operate, and produce visible separation zones, allowing for easy adjustment and monitoring. They are suitable for a wide range of particle sizes and densities.
Disadvantages: They typically have lower throughput capacity compared to some other methods like jigs or spirals. They also require a relatively large footprint and consume a significant amount of water.
Answer: The selection depends on the material being processed, the desired throughput, and the particle size range. Factors to consider include the deck area, stroke length, and riffle design. Consulting with a manufacturer or expert is recommended to determine the optimal configuration.
