全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
Sand making machine is widely used in highway, mining, gravel field, cement, coal, refractory materials, glass, cement concrete aggregate production and other industries.
A sand making machine, also known as a vertical shaft impact crusher, is a type of equipment used to crush or shape rocks into sand particles. Its main purpose is to produce well-shaped sand products that can be used as a substitute for natural sand.


A Sand Making Machine is a piece of equipment designed specifically to create sand. The most advanced and common type is the VSI Crusher. VSI stands for Vertical Shaft Impactor. Unlike other crushers that squeeze rock, a VSI crusher uses speed to shatter it.
This machine has a vertical shaft that spins a rotor at very high speeds. When you feed small rocks into the center of the rotor, centrifugal force throws them outwards. The rocks exit the rotor at speeds of 50-80 meters per second. They smash against an outer ring and shatter into smaller pieces with an excellent, cubical shape. This high-impact method is the key to producing high-quality sand.
You need this machine for three main reasons: environment, quality, and cost. Governments around the world are banning or restricting the mining of river sand. This is done to protect river ecosystems. A VSI sand maker allows you to produce sand sustainably from quarries.
Second, the quality of river sand is inconsistent. It often contains silt, clay, and organic matter that weakens concrete. With a rock sand machine, you have complete control over the final product. You can create sand with the perfect size, shape, and cleanliness. This results in stronger, more durable concrete.
Finally, relying on river sand means you are dependent on distant suppliers and high transportation costs. By producing your own sand on-site with a ZONEDING VSI, you take control of your supply chain. You reduce transport costs and ensure you always have the exact sand you need, right when you need it.
Rock, aggregate, river pebble, granite, limestone, basalt, glass, quartz, cobble, dolomite, calcite, diabase, andesite, sandstone, asphalt concrete, construction wastes, road materials, ore tailings, etc.

In order to ensure the overall performance of the equipment, the structure of key parts on Sand making machine is optimized, such as the impeller, the bearing cylinder, and the main body to ensure the high yield, high efficiency and low cost of the crushing equipment in crushing operation.
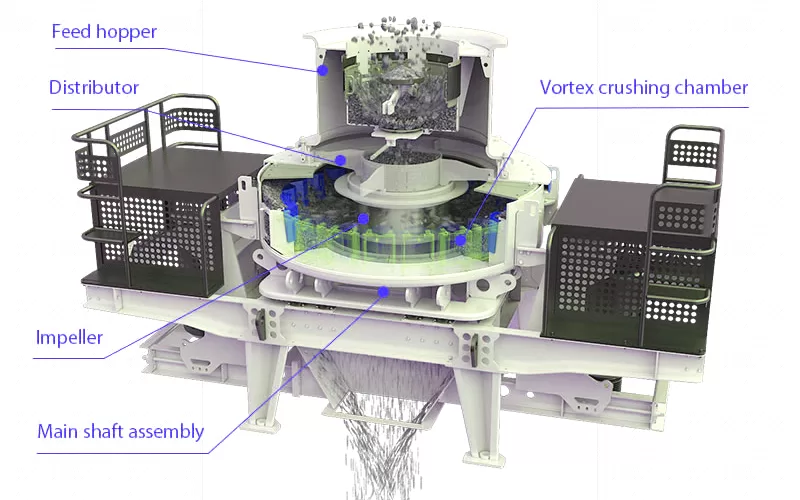
Sand Making Machine is mainly composed of feeding device, distributor, and whirling motion crushing cement clinker, quartz stone, iron ore and concrete aggregate, and especially suitable for making building sand and road paving sand and stone.
chamber, impeller, principal axis assembly, pedestal driving device and motor.
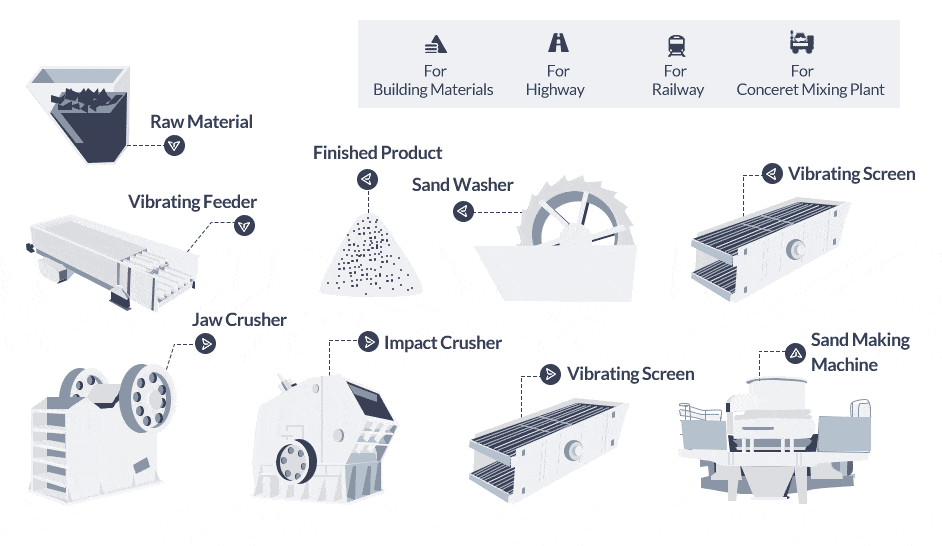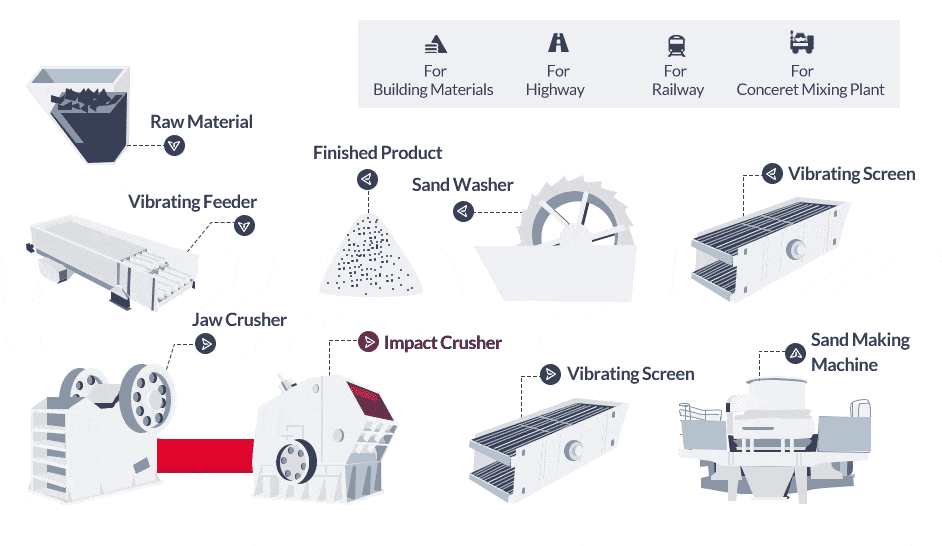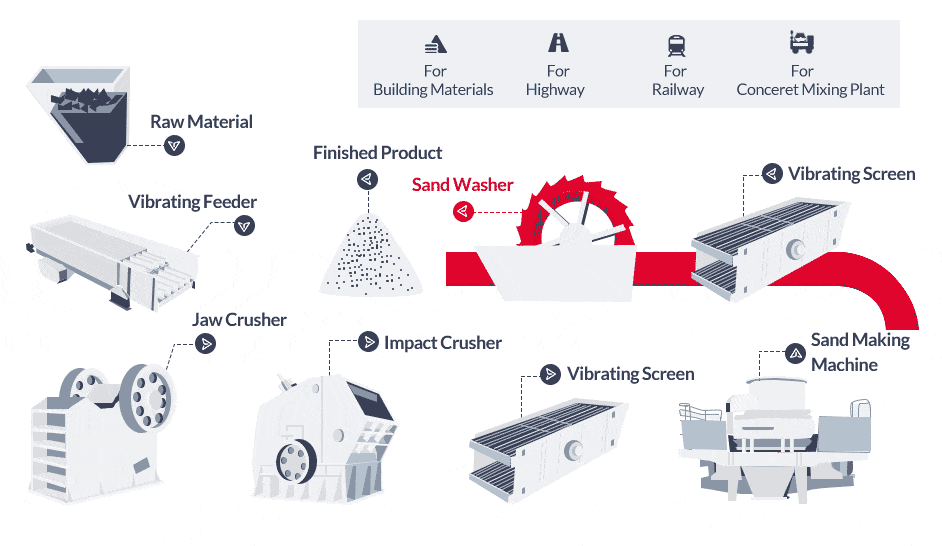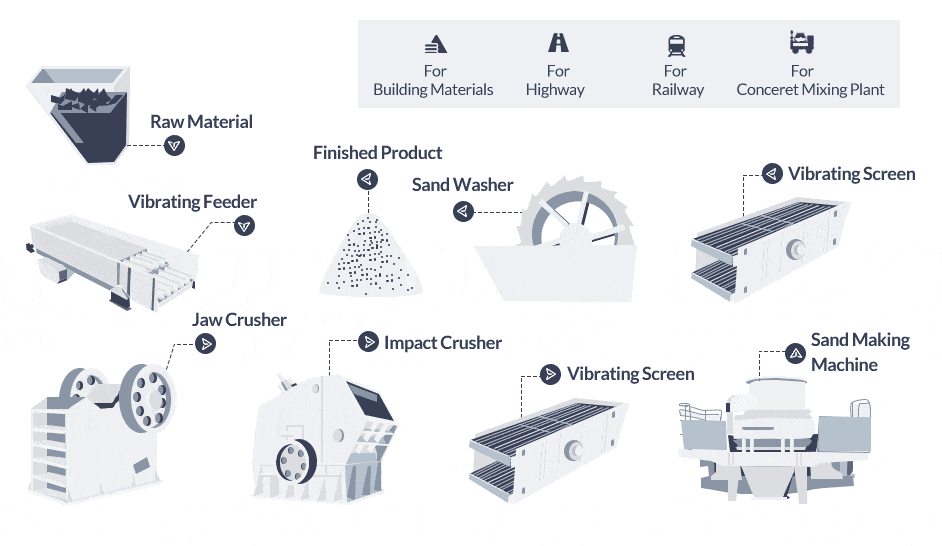
The sand making product line follows a systematic process. Here’s a clear and structured breakdown of the steps involved:
Stone Crushing: Large stone pieces stored in the silo are fed into the jaw crusher by a vibrating feeder for coarse crushing. The crushed materials are then conveyed by a belt conveyor to a cone crusher or impact crusher for further crushing.
Screening: The belt conveyor transports the crushed materials to a vibrating screen for screening. The vibrating screen separates the finished sands (materials above the sieve) from the oversized particles (materials under the sieve).
Sand Washing: The finished sands are carried by a belt conveyor to a sand washing machine for washing and removing impurities. After washing, the cleaned sands are sent to the finished product stack with the help of a belt conveyor.
Fine Crushing: The oversized particles (materials under the sieve) are conveyed by the belt conveyor to a vertical mobile impact crusher (artificial sand making machine for sale) for fine crushing. The finely crushed stones are then sent back to the vibrating screen for another round of screening.
This process forms a closed loop where the materials go through repeated crushing and screening stages until they meet the desired size and quality requirements. The rock crusher equipment continues until the desired amount of sand is produced. By following this structured sand processing line, sand manufacturing machines efficiently crush, screen, wash, and refine raw materials to produce high-quality sand products. Let’s take a look at a real case.
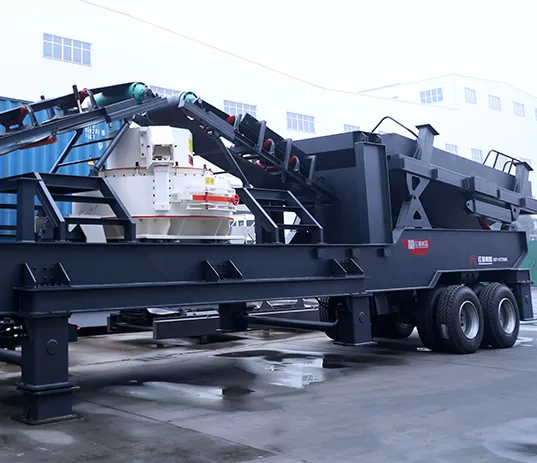
Our most popular sand making machines currently are the VSI, PCL, and mobile models. PCL sand makers are the most advanced and suitable for sand making manufacturers with high requirements on finished products and sufficient budget. VSI sand makers are cost-effective. Mobile sand makers can meet the portable and mobile sand making needs.
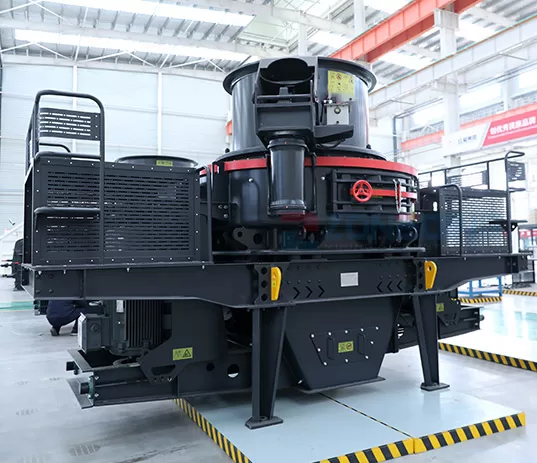
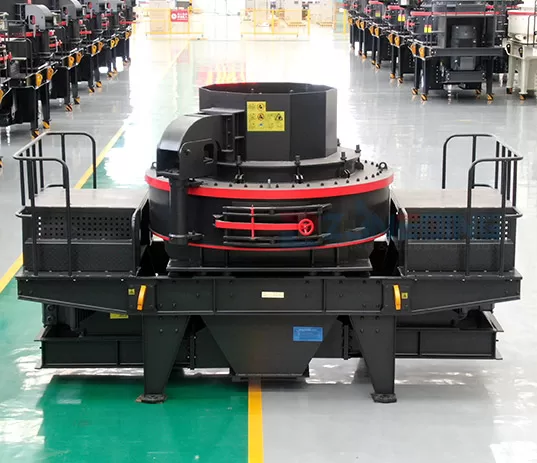



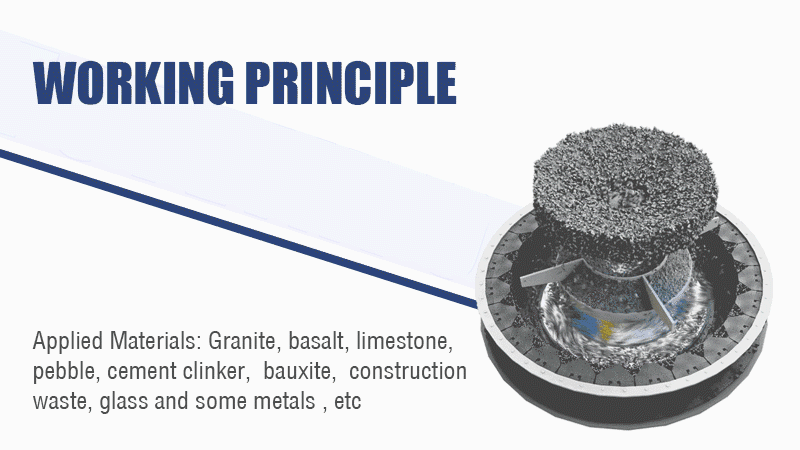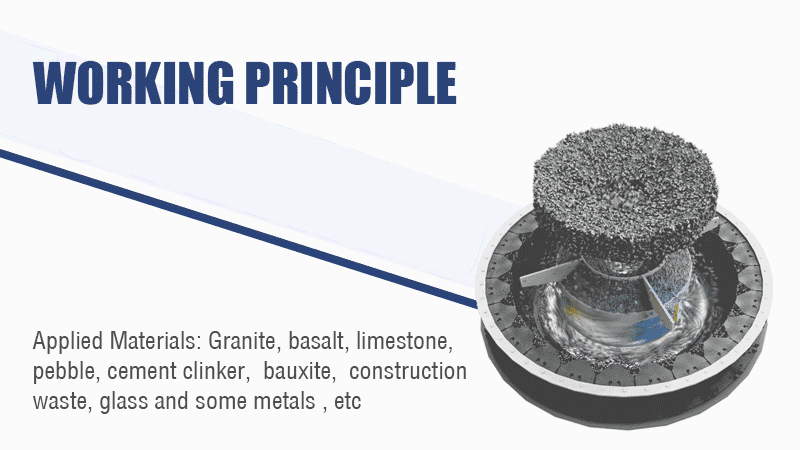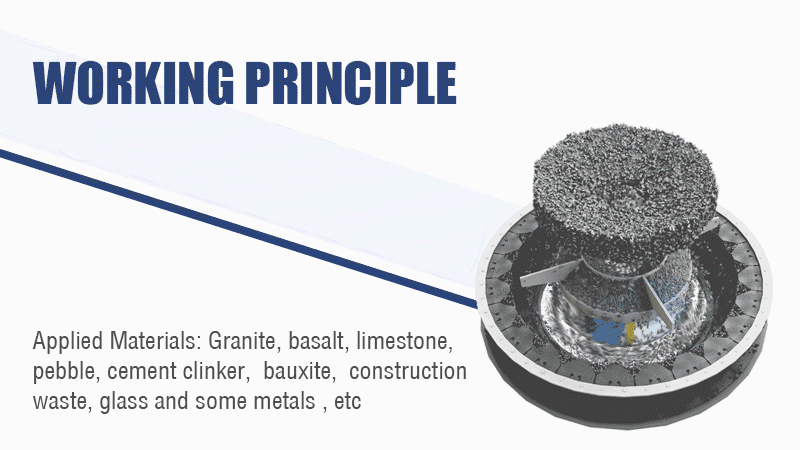
The sand making machine uses the working principle of high-speed impact and crushing:
1. First the material flows into the vortex crushing cavity from the feed hopper. The high-speed rotating impeller crushes the material scattered around the impeller in the form of an umbrella.
2. After the materials collide with each other, the material layer between the impeller and the casing will form a vortex flow for multiple collisions, friction, and crushing.
3. Then the material is discharged from the lower discharge hopper to complete the crushing process. The particle size of the finished product is controlled by the screening machine.
| Model | Sand Shaping | Sand Making | Sand Shaping | Sand Making | Motor Power(kw) |
| Max.Feeding Size (mm) | Throughput(t/h) | ||||
| PCL 0815 | <30 | <35 | 70-140 | 130-230 | 2×75 |
| PCL 0818 | <30 | <35 | 80-190 | 165-283 | 2×90 |
| PCL 0922 | <35 | <40 | 105-145 | 220-330 | 2×110 |
| PCL 0926 | <35 | <40 | 120-190 | 240-380 | 2×132 |
| PCL 1032 | <40 | <45 | 181-278 | 246-356 | 2×160 |
| PCL 1040 | <40 | <45 | 262-284 | 350-440 | 2×200 |
| PCL 1250 | <45 | <50 | 345-371 | 414-540 | 2×250 |
| PCL 1263 | <50 | <55 | 453-498 | 521-585 | 2×315 |



Adjust rotor speed (higher = finer, more cubical), cascade feed ratio, and feed size. Proper feed prep is key.
Distributor plate, feed eye ring, wear plates/liners. Use high-quality alloys, ensure balanced rotor, regular inspection.
VSI for superior cubicity, finer product, and tertiary/shaping stage. Cone often for coarser sand or secondary crushing.
Reduces efficiency, can cause rotor/chamber blockages, increases power draw, accelerates wear. Pre-screening/washing vital.
Rock-on-rock: better cubicity, less metallic wear, more fines. Rock-on-anvil: higher output, more controlled fines, higher wear part cost.
