全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
Shaking table is also called shaker table, which is the commonly used gravity ore dressing equipment. Its separation efficiency is greater than the general gravity separation equipment.
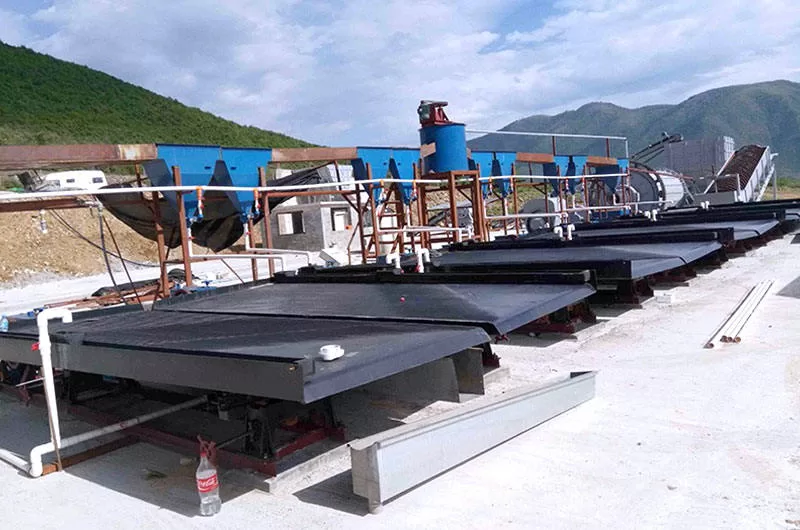
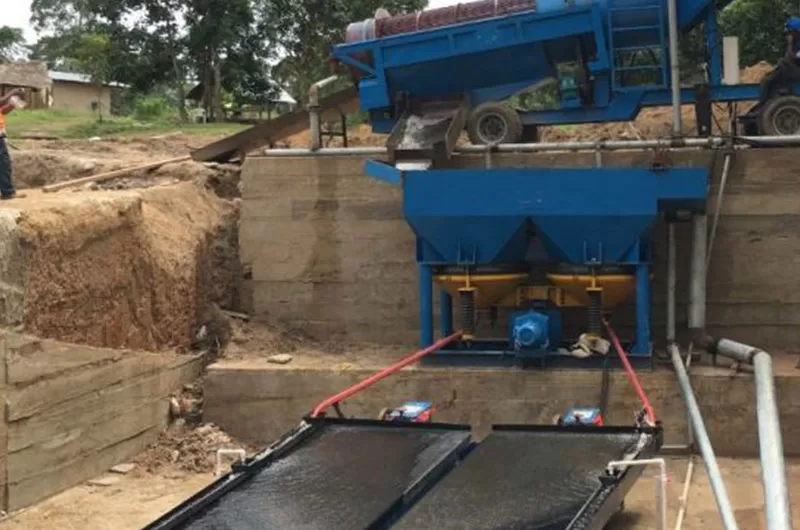
Shaking table is a kind of gravity beneficiation equipment, which is mainly used for separating gold, silver, lead-zinc, tantalum-zinc, tin and other rare metal and precious metal ores. The role of shaking table is similar to centrifugal gold concentrator, belongs to alluvial gold washing ore dressing equipment, rarely used in alluvial gold ore roughing, mostly used in alluvial gold ore rough concentrate ore dressing and purification. It can extract high purity gold.


Shaking table gold separation is suitable for processing minerals with finer particle size. According to the particle size of the ore, it can be divided into three types: coarse sand bed, fine sand bed and ore mud bed. Among them, the coarse sand bed is suitable for separating material particle size For ore particles as small as 0.5 mm, the fine sand bed is suitable for processing ore particles with a particle size range of 0.5 to 0.074 mm, and the ore mud bed is suitable for processing ore particles with a particle size of 0.074 to 0.037 mm.

Bed head: contains the electric motor, transmission device, to provide power for the shaking table.
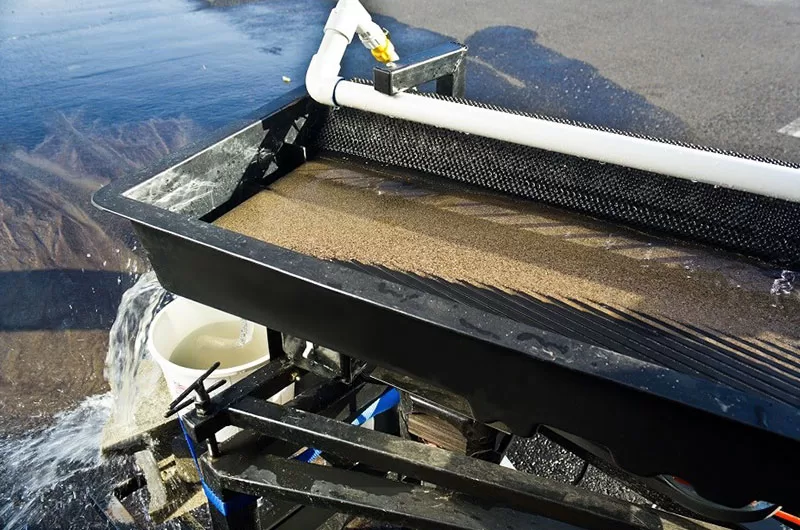
Bed surface: the working area for ore sorting, made of wear-resistant material with bed strips.
Slope adjuster: used to adjust the inclination angle of the bed to optimize the sorting effect.
Water Tank: Provides the water flow required for sorting to help loosen and stratify the ore.
Tanks: hold the ore to be sorted.
Rifling bars: guide the movement of the ore on the bed.
Lubrication System: Ensures smooth operation of shaking table components and reduces wear and tear.
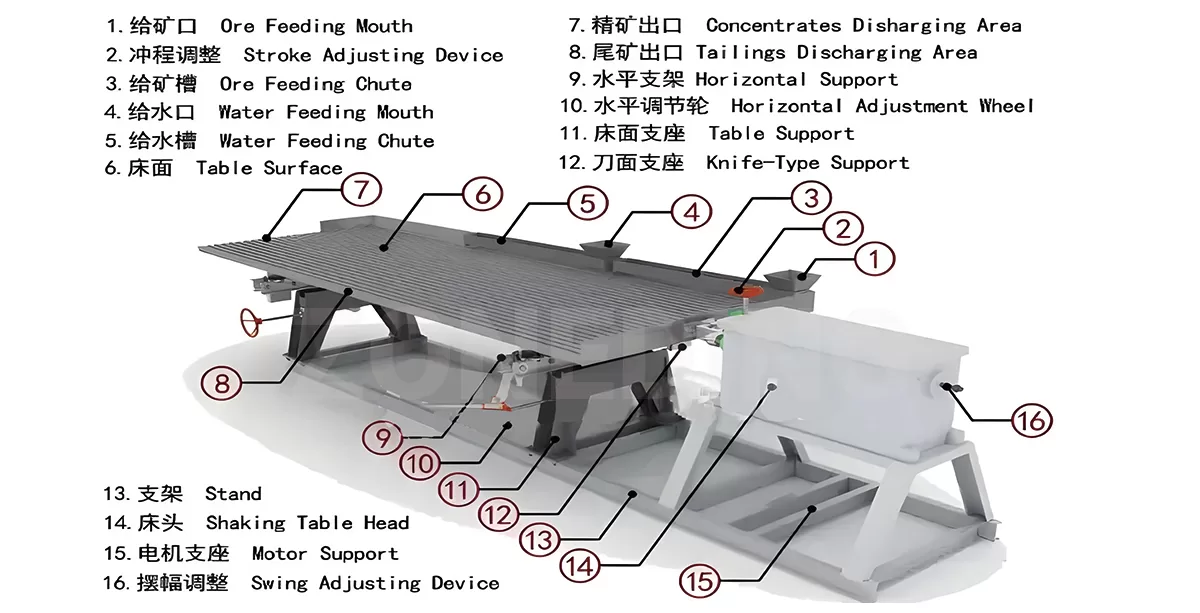
The shaking table of Zhongding machine mainly relies on its unique shaking trajectory and bed design to realize the separation of minerals. When the motor starts, the power is transmitted to the crankshaft of the shaking table through the transmission device such as belt or gear. The crankshaft then rotates, driving the connecting rod and rocker for up and down or back and forth reciprocating motion. This movement makes the bed surface produce certain vibration and tilt, so that the mineral particles in the bed surface for layering and movement.
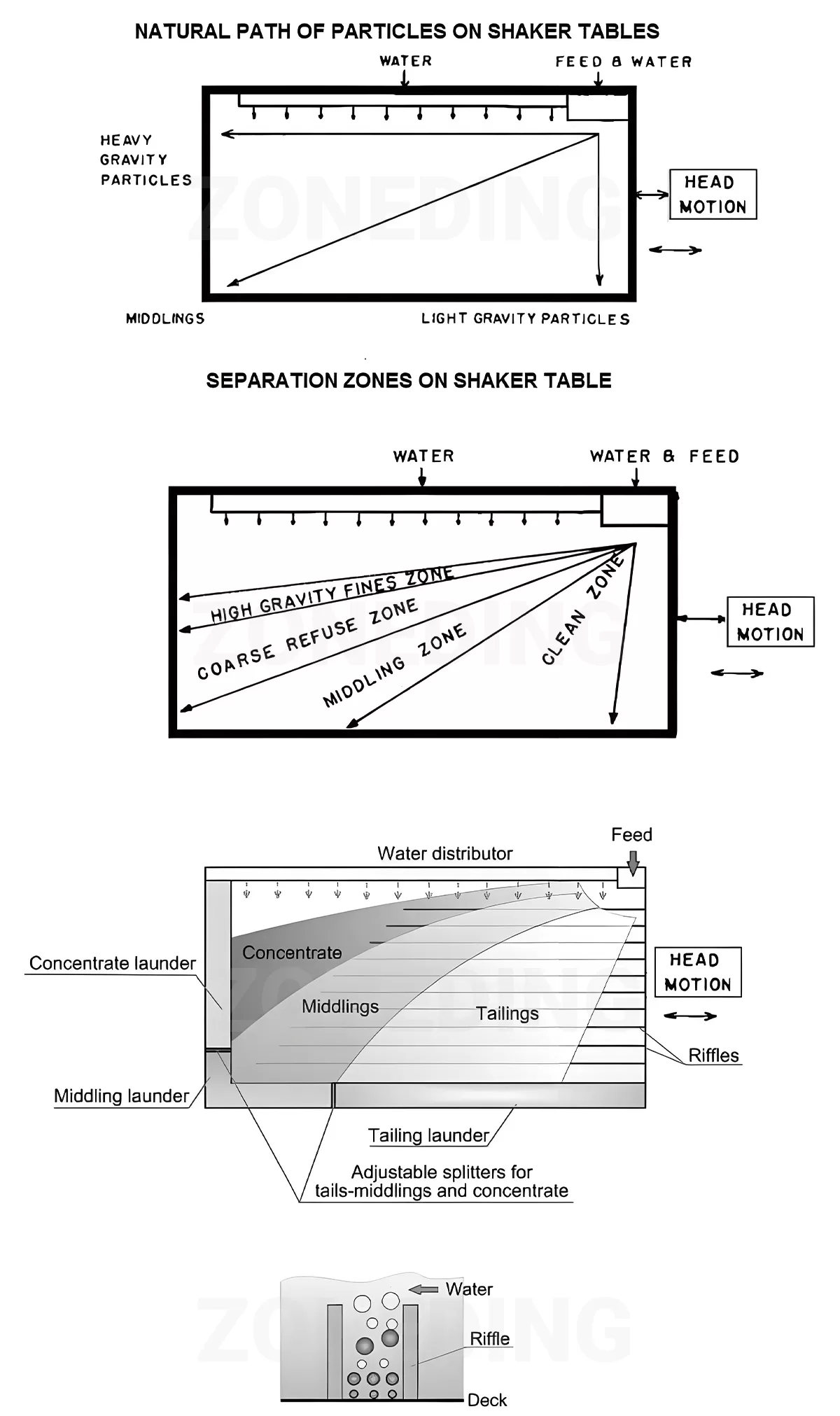
As mineral particles of different densities have different settling speeds under the combined effect of vibration and water flow, they will be gradually stratified and moved to different positions on the bed in the order of density from low to high. Eventually, by adjusting the tilt angle of the bed and vibration parameters, the mineral particles of different densities can be discharged from the concentrate and tailings ports of the bed, thus realizing the effective separation of mineral.
| Name | Grit concentrator table | Fine sand concentrator table | Sludge concentrator table | |
| Bed surface Dimensions | Length(mm) | 4450 | 4450 | 4450 |
| Driving part Width(mm) | 1855 | 1855 | 1855 | |
| Concentrate part Width(mm) | 1546 | 1546 | 1546 | |
| Max.feeding size(mm) | 2 | 0.5 | 0.15 | |
| Feeding amount(t/d) | 30-60 | 10-20 | 15-25 | |
| Feeding thickness(%) | 25-30 | 20-25 | 15-25 | |
| Stroke(mm) | 16-22 | 11-16 | 8-16 | |
| Frequency(f) | 45-48 | 48-53 | 50-57 | |
| Bed surface Water quantity(t/d) | 80-150 | 30-60 | 10-17 | |
| Bed surface Horizontal obliquity(°) | 2.5-4.5 | 1.5-3.5 | 1-2 | |
| Bed surface Portrait obliquity(%) | 1.4 | 0.92 | —- | |
| Table board corner(°) | 32-42 | 40 | 42 | |
| Concentrating area(㎡) | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.6 | |
| Bed surface Length ratio | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | |
| Shape of side-bed surface | Rectangle | Zigzag | Triangle | |
| Motor power(kw) | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | |
| Transmission device | Eccentricity Linkage | |||



Answer: Key factors influencing separation include the table’s motion (stroke and frequency), water volume and slope, feed rate and concentration, and the feed material’s particle size and shape. Proper adjustment of these factors is critical for efficient separation. The table’s longitudinal and transverse slopes must be precisely controlled. The feed concentration should also be appropriate, typically 20-30% for coarse minerals and 15-25% for fine minerals.
Answer: Operation involves observing the bed surface and adjusting the slope, water flow, and feed rate. Regular maintenance includes checking for loose parts, lubricating moving components, inspecting for wear, and cleaning the table surface. Preventative maintenance should be performed regularly, with intervals ranging from every month to once a year.
Answer: Common issues can include table shaking or choppy cuts, uneven material distribution, or poor separation. Troubleshooting may involve checking for loose bolts, damaged springs, or misalignment, adjusting belt tension, inspecting electrical components, and ensuring proper lubrication. If there’s unusual noise, identify the source and eliminate the problem.
Answer:
Advantages: Shaking tables offer high enrichment ratios, are relatively simple to operate, and produce visible separation zones, allowing for easy adjustment and monitoring. They are suitable for a wide range of particle sizes and densities.
Disadvantages: They typically have lower throughput capacity compared to some other methods like jigs or spirals. They also require a relatively large footprint and consume a significant amount of water.
Answer: The selection depends on the material being processed, the desired throughput, and the particle size range. Factors to consider include the deck area, stroke length, and riffle design. Consulting with a manufacturer or expert is recommended to determine the optimal configuration.
