全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
Rod mills have two types dry type rod mill and wet type rod mill. Inside the rod mill, there are many wear resistant steel bars, and the steel bar length is 10%-15% shorter than the length of the equipment itself.
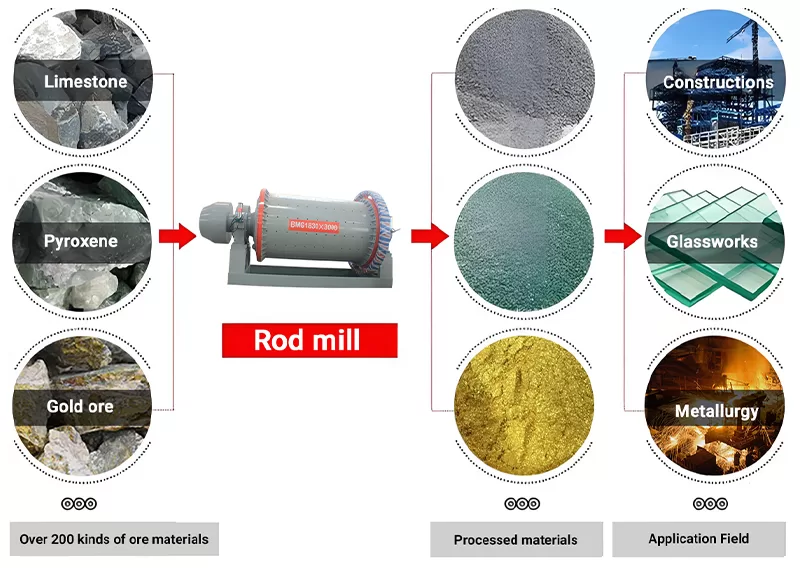
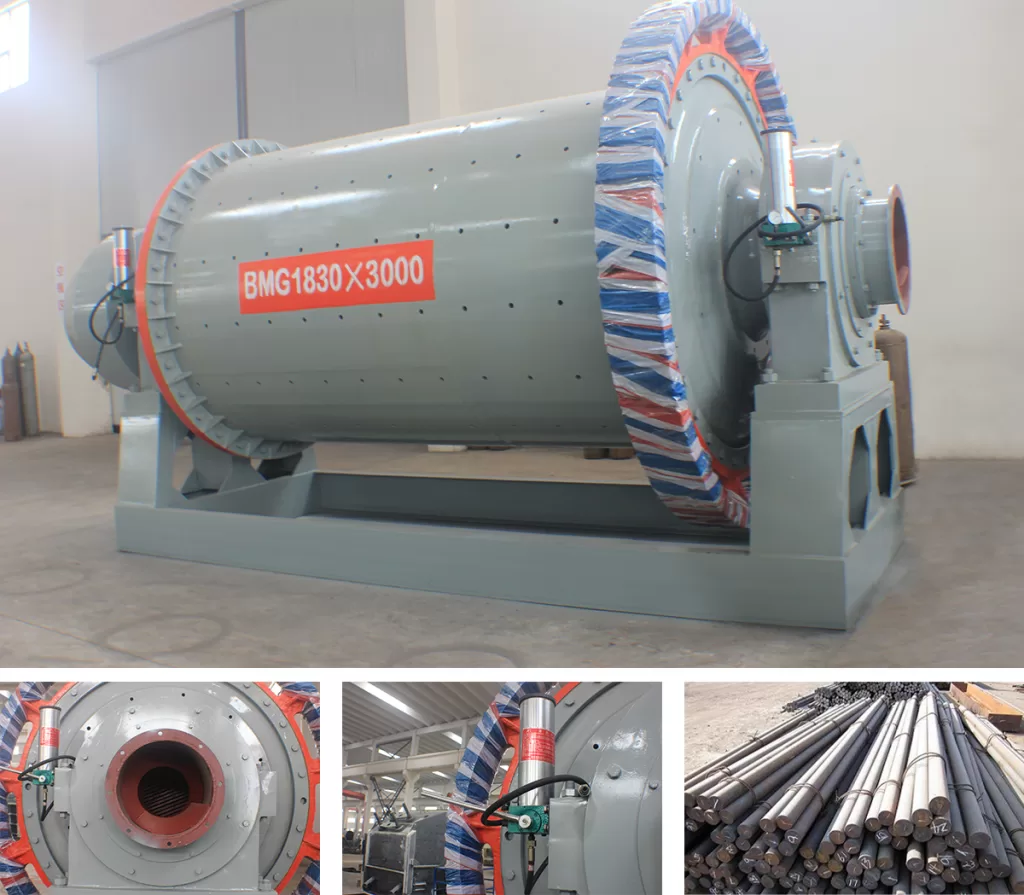
The rod mill is named after the grinding body loaded in the cylinder is a steel rod. The rod mill crusher is generally a wet overflow type and can be used as a first-level open-circuit grinding. The rod mill machine is widely used in metal and non-metal mines. And water conservancy and building materials departments to grind various ores or rocks.
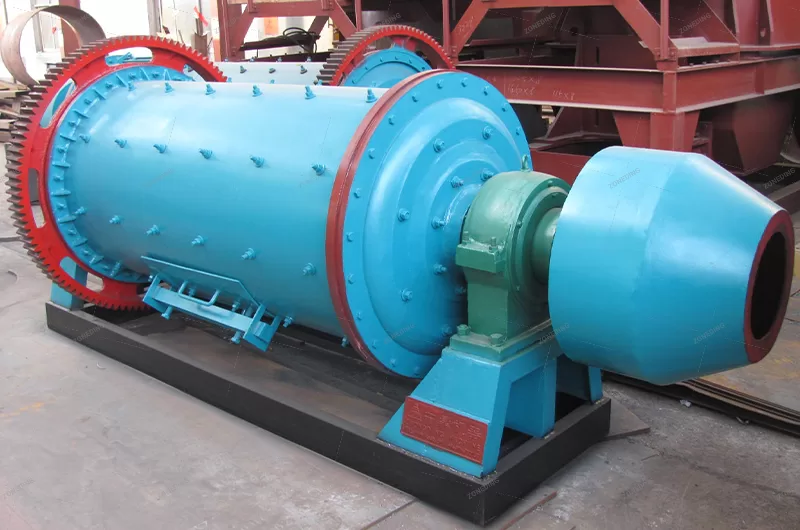
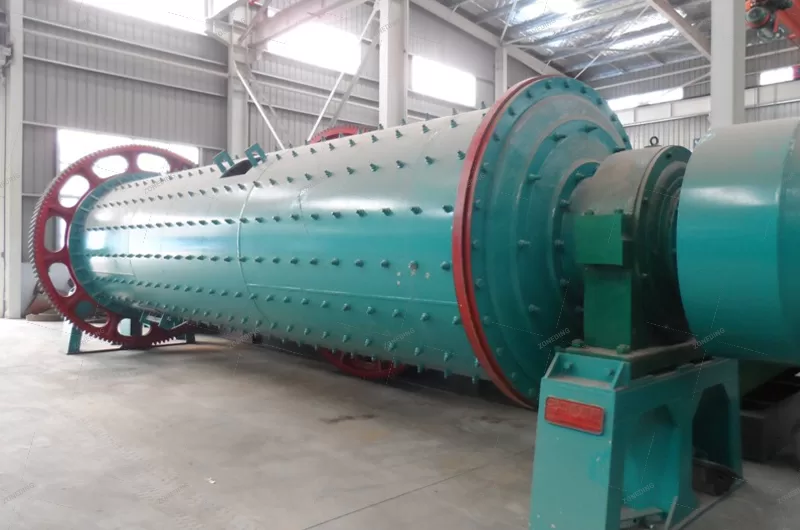


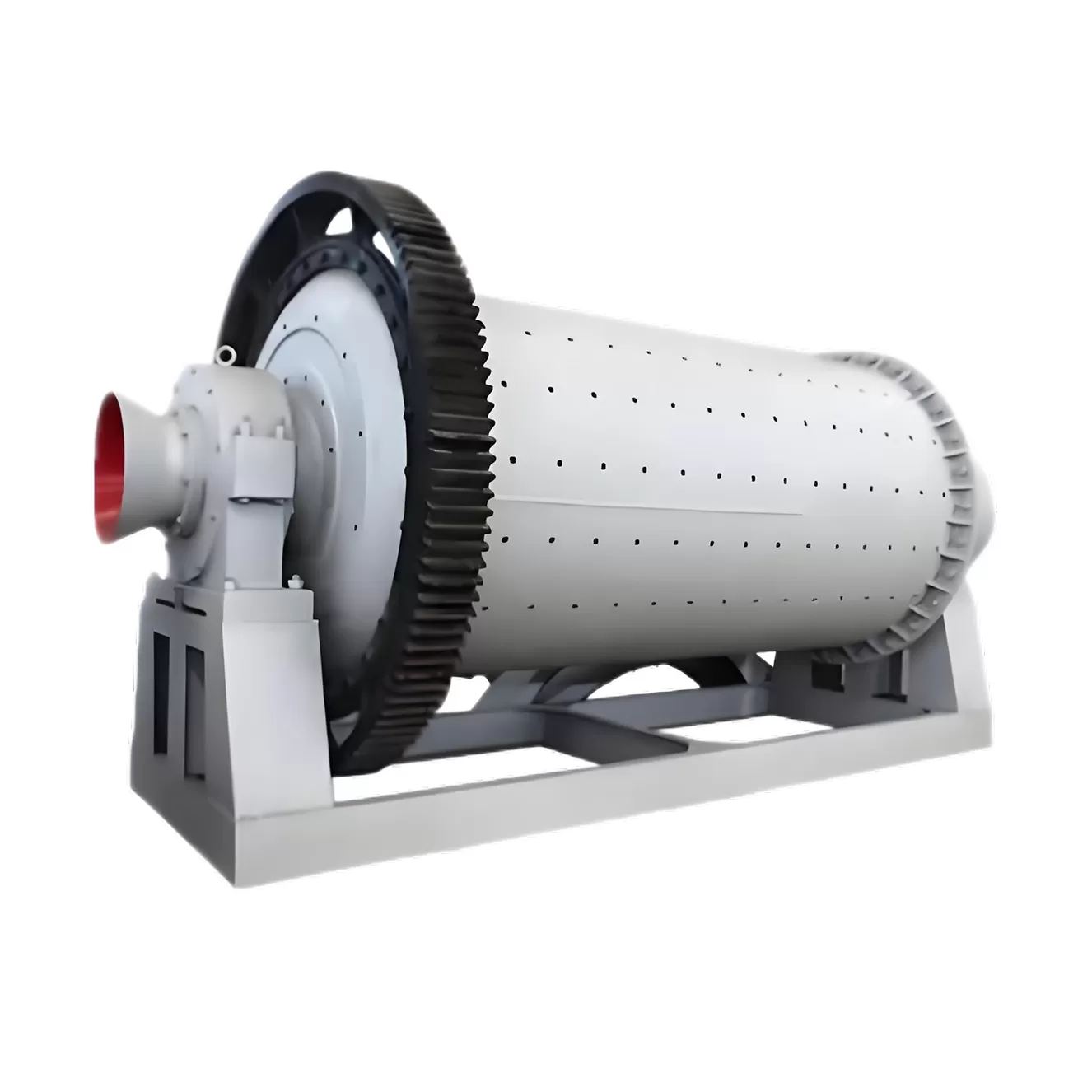
The rod mill is a specific type of grinding equipment known for utilizing long steel rods as its grinding media. It sees extensive use across diverse sectors such as metal and non-metal mining, water conservancy projects, building materials production, chemical processing, refractories, metallurgy, and the glass industry. This equipment often features advanced, controllable feeding and discharging systems, matched with appropriate rod charges for the specific material. This design promotes line contact grinding, differing from point or surface contact, which typically results in a more uniform particle size in the output and increased production capacity. Rod mills are available in both dry and wet grinding configurations, offering flexibility for users based on their particular needs and circumstances.

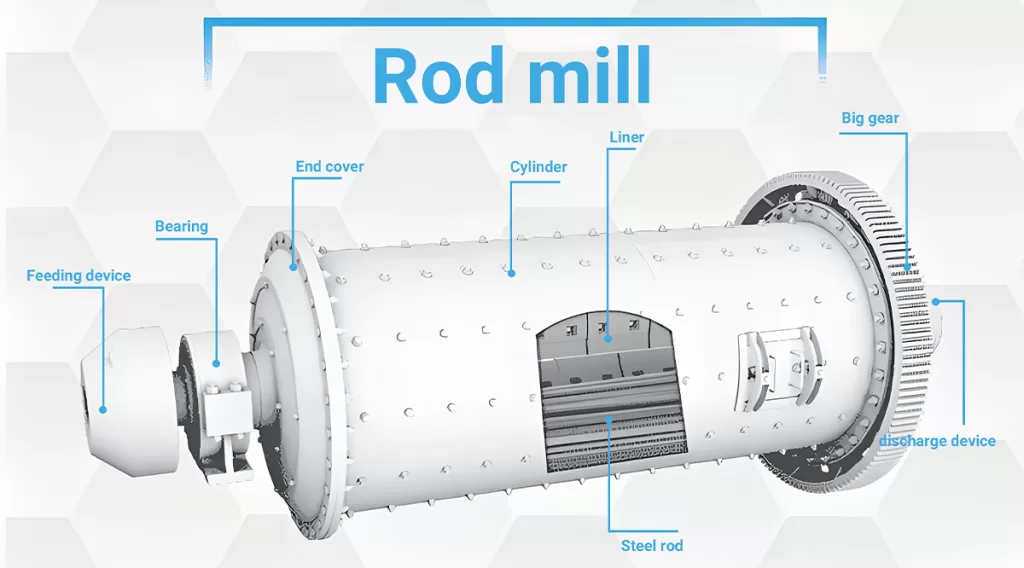
The feeding device is a shoe-shaped hopper, and the upper flange is connected with the feeding equipment to receive the fed material. There is an inspection door on the back wall of the hopper, forming a round tube and extending into the spiral barrel mounted on the hollow shaft, through which the material enters the mill.
The rotating part is a cylinder rolled and welded by steel plates. A liner is arranged inside the cylinder, which not only protects the cylinder but also lifts the steel rod to a suitable height to improve the efficiency of sand making. There is an acid and alkali resistant rubber pad between the steel liner and the simplified end cover to reduce noise and vibration.
The large and small gears are driven by helical gears with balanced work, small impact and long life. It adopts spray lubrication and regular oil injection, which reduces the labor intensity of workers, has a good lubrication effect and reduces the consumption of lubricating oil.
The main bearing supports all the weight of the rotating part, steel bars, materials, etc. The bearing bush is supported on the spherical seat, which can play a self-defense function to adapt to manufacturing and installation errors.
After the long-term work of the main bearing, the bearing bush will wear and tear, resulting in the sinking of the hollow shaft. The sealing bracket can be adjusted downward to ensure that the seals and the hollow shaft are in good contact.
The barrel of the wet/dry rod mill rotates at a certain speed, and the grinding body rises to a certain height under the action of friction and centrifugal force and is thrown down, so that the material is impacted and ground to achieve the purpose of grinding.
The rods have a screening effect on the materials during movement, which can make the large particle material be lifted to the high position of each layer and concentrated to the place with strong crushing ability. Therefore, the working efficiency of the rod mill is high and the power consumption is low.
When the ore is ground by the steel rod, it is first crushed into coarse particles and then ground into smaller ones, thereby reducing the risk of over-crushing.

| Model | Shell rotation speed(r/min) | Feeding size(mm) | Discharging size(mm) | Processing capacity (t/h) | Power (kw) | Total weight (t) |
| MBS0918 | 36-38 | ≤25 | 0.833-0.147 | 0.62-3.2 | 18.5 | 5.9 |
| MBS0924 | 36 | ≤25 | 0.833-0.147 | 0.81-4.3 | 22 | 6.7 |
| MBS1224 | 36 | ≤25 | 0.833-0.147 | 1.1-4.9 | 30 | 13.9 |
| MBS1530 | 29.7 | ≤25 | 0.833-0.147 | 2.4-7.5 | 75 | 19.8 |
| MBS1830 | 25.4 | ≤25 | 0.833-0.147 | 4.8-11.6 | 130 | 34.9 |
| MBS2130 | 23.7 | ≤25 | 0.833-0.147 | 14-35 | 155 | 46.5 |
| MBS2136 | 23.7 | ≤25 | 0.833-0.147 | 19-43 | 180 | 48.7 |
| MBS2430 | 21 | ≤50 | 0.833-0.147 | 25-65 | 245 | 59.7 |
| MBS2736 | 20.7 | ≤50 | 0.833-0.147 | 32-86 | 380 | 92.5 |
| MBS2740 | 20.7 | ≤50 | 0.833-0.147 | 32-92 | 400 | 95 |
| MBS3245 | 18 | ≤50 | 0.833-0.147 | 64-180 | 630 | 149 |



A Rod Mill is a grinding machine that uses steel rods as the grinding media to reduce the size of materials.
A Rod Mill rotates horizontally, causing steel rods to tumble and grind material through impact and attrition.
Rod Mills produce a coarser product compared to ball mills and are suitable for preparing feed for downstream processes, minimizing fines.
Rod Mills are used for grinding ores, minerals, aggregates, and other materials in mining, construction, and chemical industries.
Consider feed size, desired product size, mill capacity, rod charge, and material abrasiveness when selecting a Rod Mill.
