全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
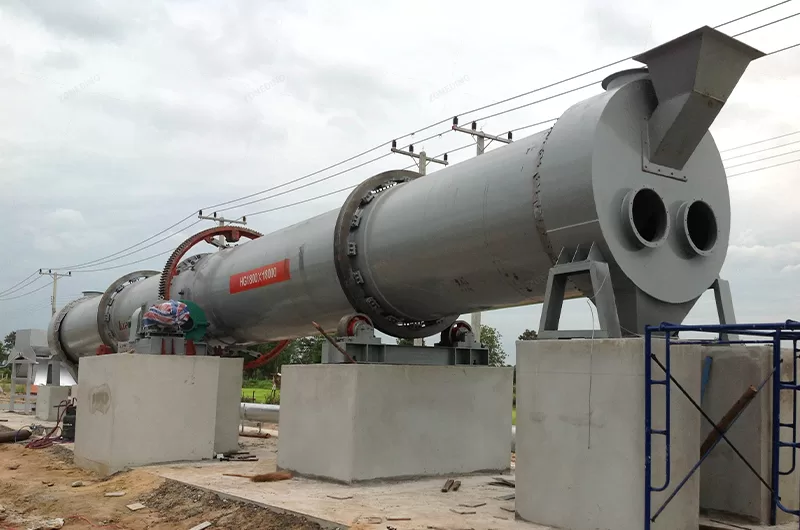
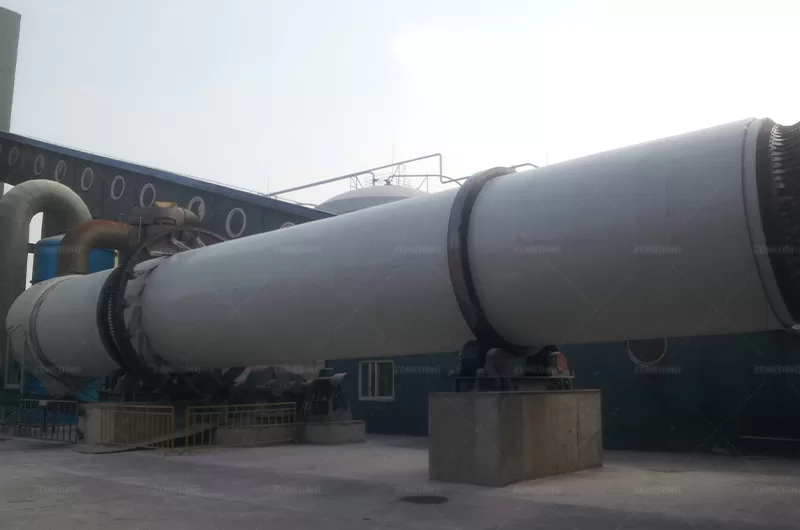
Rotary coolers are designed to cool down products coming from dryers or calciners up to an acceptable temperature for successive handling.
A Rotary Cooler is an industrial machine specifically designed to cool the material seems like a necessary final step.
A high-efficiency rotary cooler does much more than just lower temperature. It’s crucial for recovering valuable heat (saving fuel!), stabilizing product quality, minimizing dust emissions, and enabling safe downstream handling and storage.
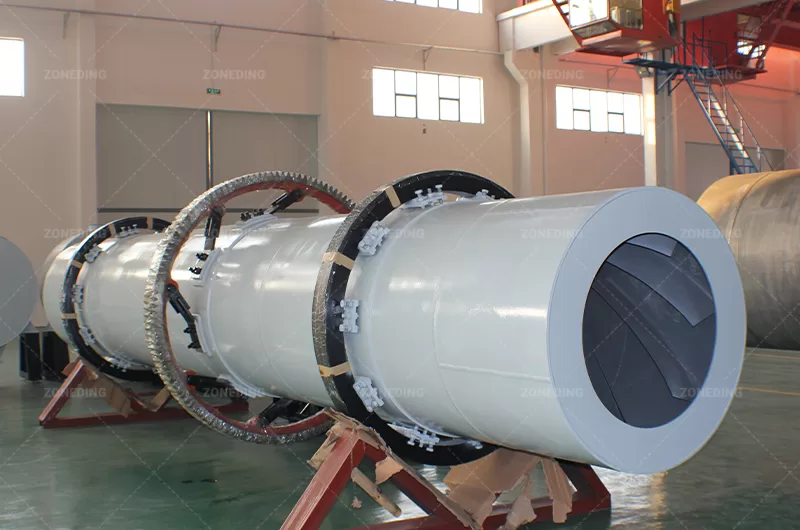
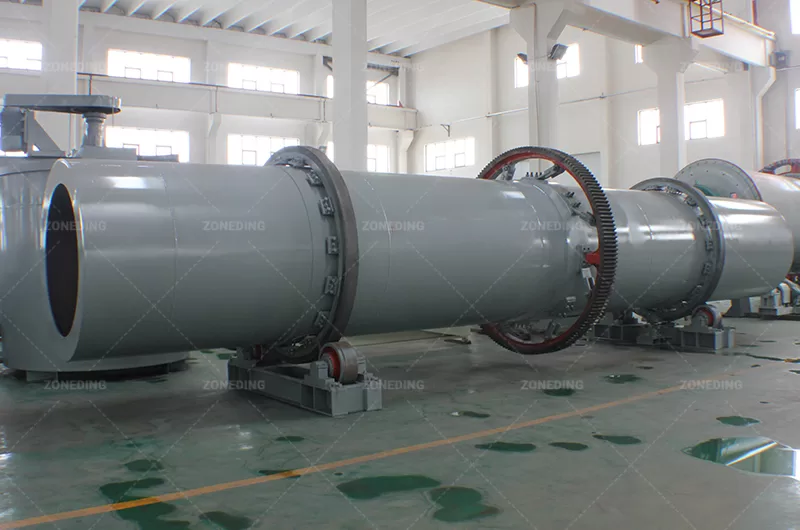


It directly mirrors the robust construction of rotary kilns and dryers, designed for continuous, demanding industrial environments.
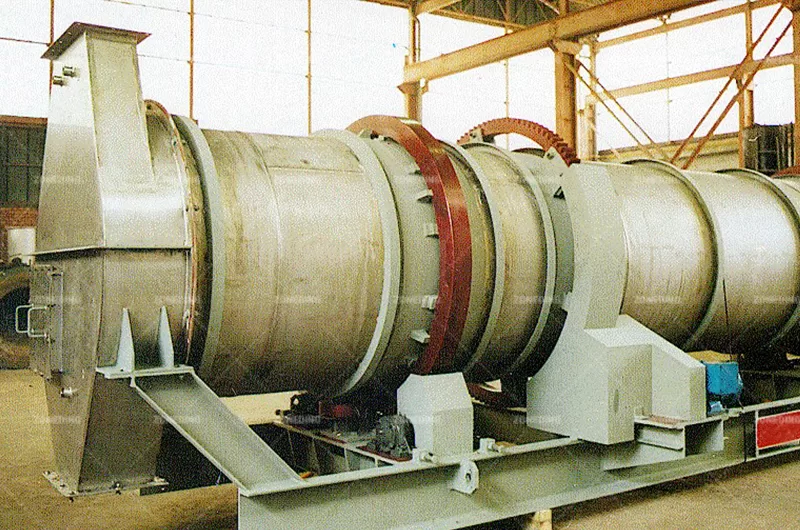
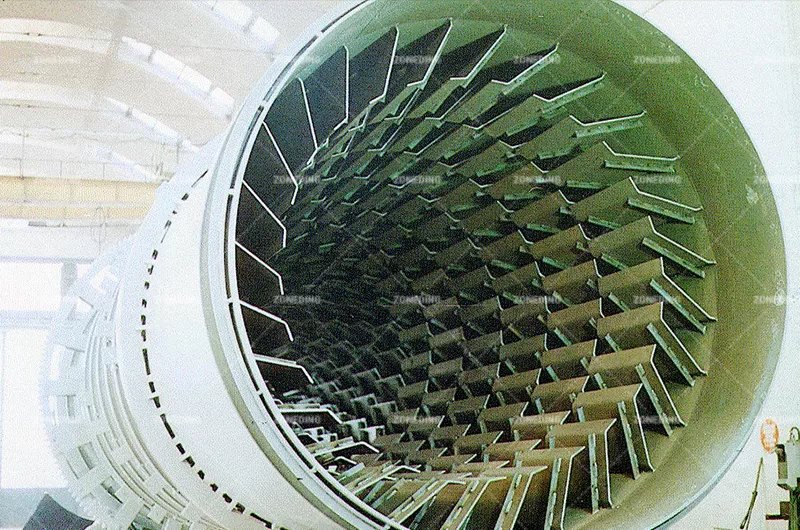
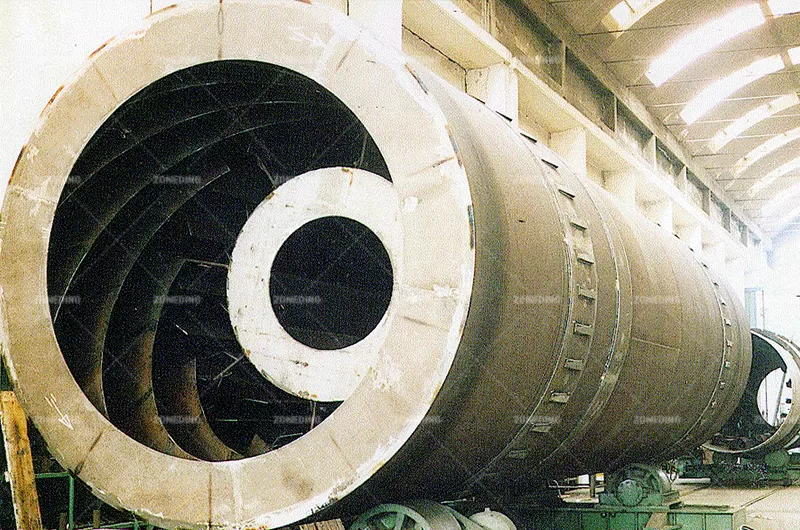

Hot material enters the elevated end and tumbles through the rotating drum. Simultaneously, cool ambient air flows through the drum (usually counter-current to material flow), making direct contact with the hot material, absorbing its heat before exiting.
ZONEDING can propose four different kinds of rotary coolers in function of inlet temperature of product, desired outlet temperature and of type of product as well as:
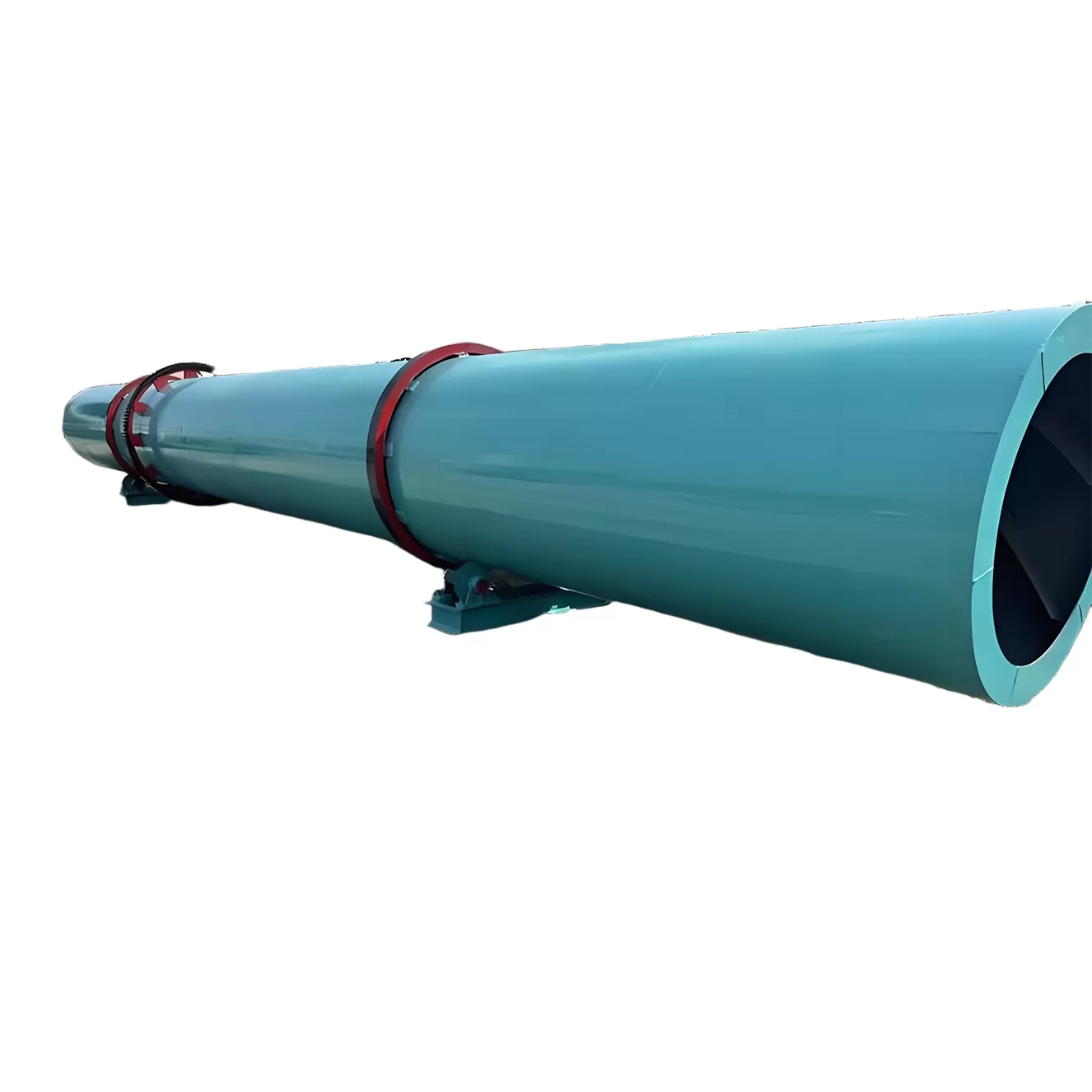
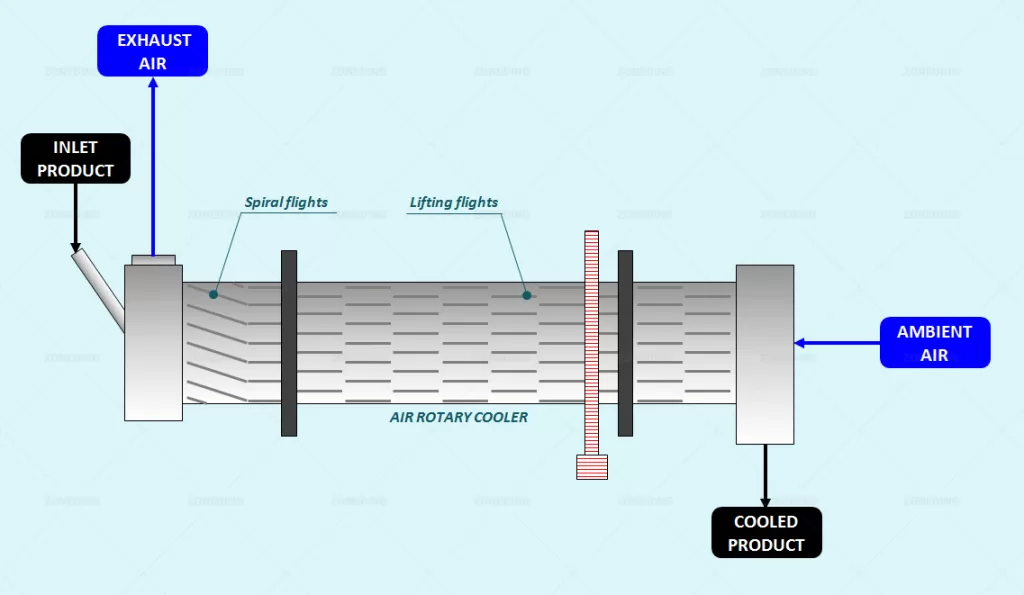
Air Rotary Coolers
Construction of Air Rotary Coolers is similar to Direct Rotary Dryers.
The product is fed inside a cylinder internally provided with spiral and lifting flights in order to achieve the contact between fresh air and the hot product to be cooled.
The heat of product is dissipated by convection by a stream of fresh air which flows in counter current configuration.
Air Rotary Coolers are mostly applied to cool down product at exit of Direct Rotary Dryers (temperature approx 100 °C).
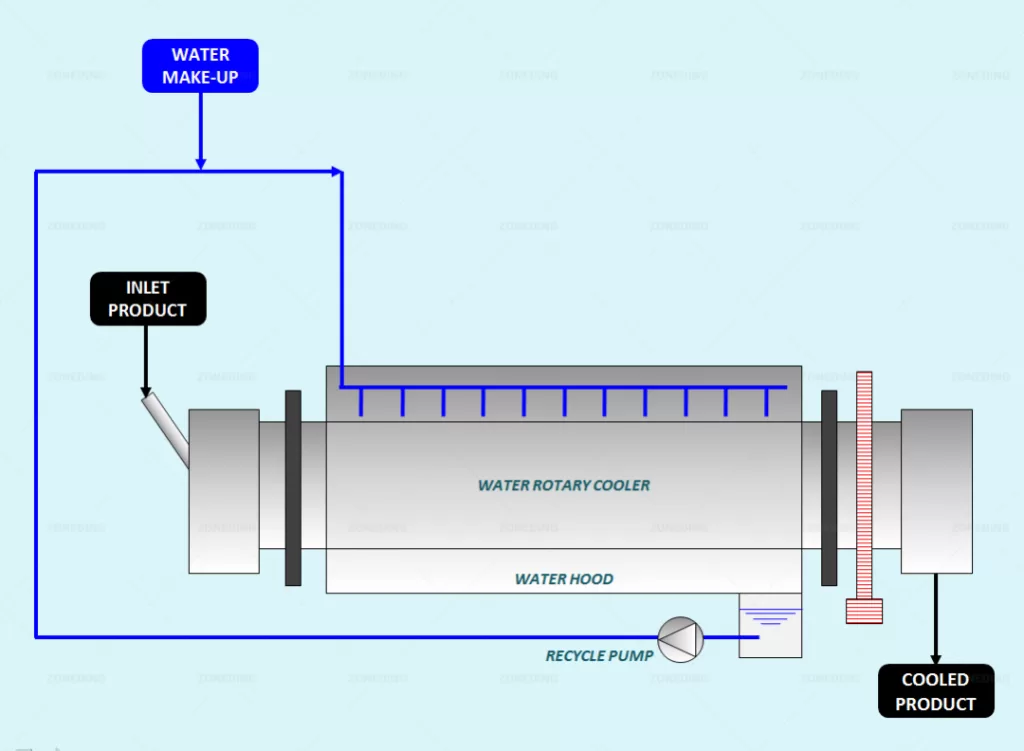
Water Rotary Coolers
In Water Rotary Coolers heat transfer occurs by radiation since water is sprayed against the wall of a rotating cylinder.
Sprayed water that did not evaporate is collected in the bottom of a hood and then recycled to the spraying device.
Cylinder can also consist of a various number of tubes connected each other in order to increase the cooling efficiency.
Water Rotary Coolers find application to cool down products at higher temperatures than the ones operated with Air Rotary Coolers (up to 900 °C and more) and for dusty products and products that cannot go in contact with air.
| Feature | Direct Rotary Cooler | Indirect Rotary Cooler |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Medium | Air (directly contacts material) | Water or Air (separated from material) |
| Mechanism | Convection between air & material | Conduction through shell/tubes |
| Heat Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Pros | Simpler design, Lower cost, Higher efficiency | Protects material from air/contamination, Handles very fine dusts, Allows inert atmosphere |
| Cons | Potential dust carry-over, Material must tolerate air contact | More complex structure, Higher cost, Lower efficiency, Potential for leaks (water tubes) |
| Typical Use | Cement clinker, Lime, Ores, Aggregates | Sensitive chemicals, Fine powders, Materials needing inert atmosphere, Food grade products |
Rotary coolers are workhorses in industries like cement (cooling clinker), lime (cooling calcined lime), mining/metallurgy (cooling sintered ores, pellets), chemicals (cooling various calcined products, fertilizers), and sometimes aggregates (cooling dried sand/gravel).



They are essential wherever bulk solids need their temperature drastically reduced after a high-temperature thermal process.
Essentially, any industry performing high-temperature calcination, sintering, roasting, or drying of bulk solids is a potential user of rotary coolers.
Key selection factors include detailed material properties (flow, temperature, stickiness), required throughput, target temperature drop, cooling type (direct/indirect), internal design (lifters), construction materials for heat/abrasion resistance, and robust drive/support systems. Considering the entire system, including airflow and heat recovery, is crucial.
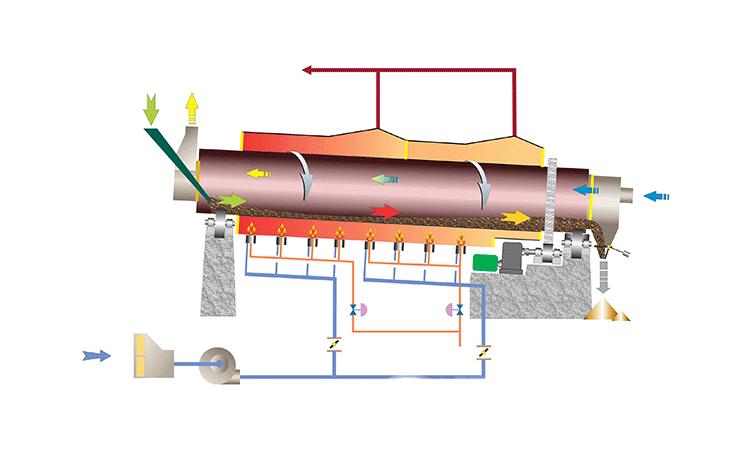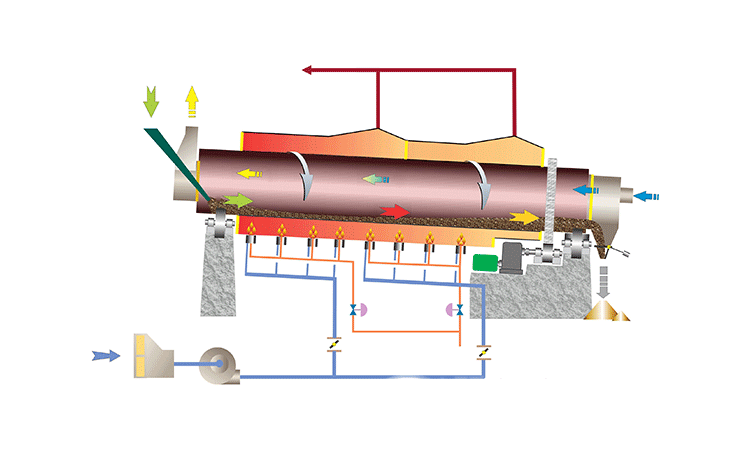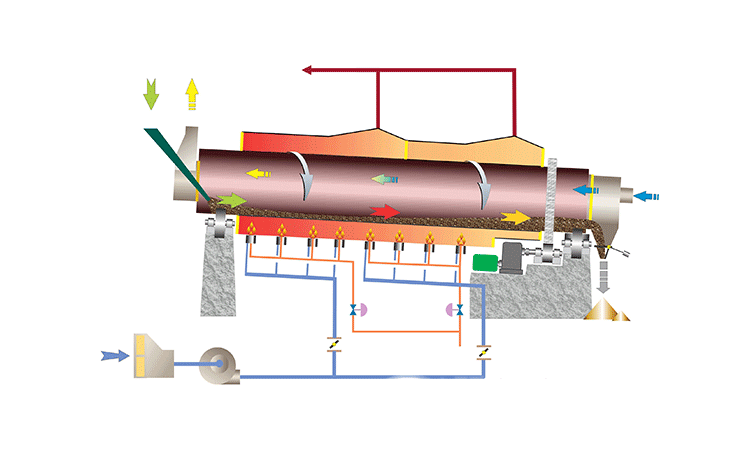
ZONEDINGMACHINE has proven experience on cooling your specific material, strong engineering capabilities for customization, high manufacturing quality standards, comprehensive installation and commissioning support, and responsive after-sales service including readily available spare parts.
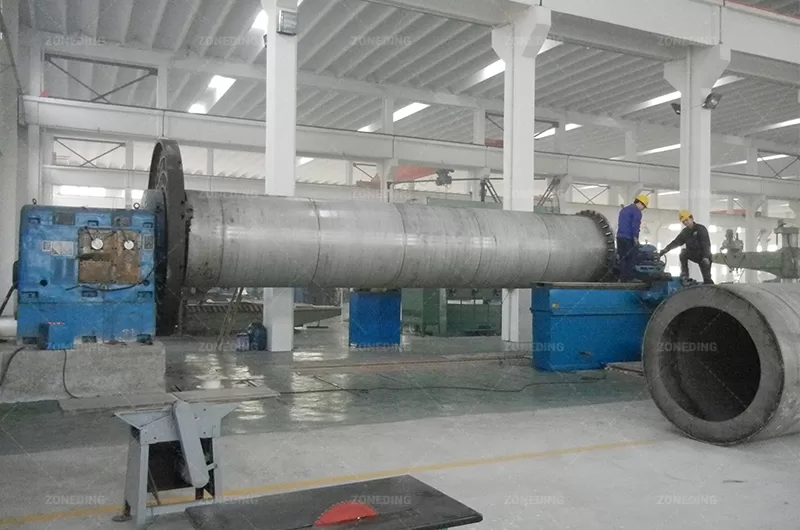
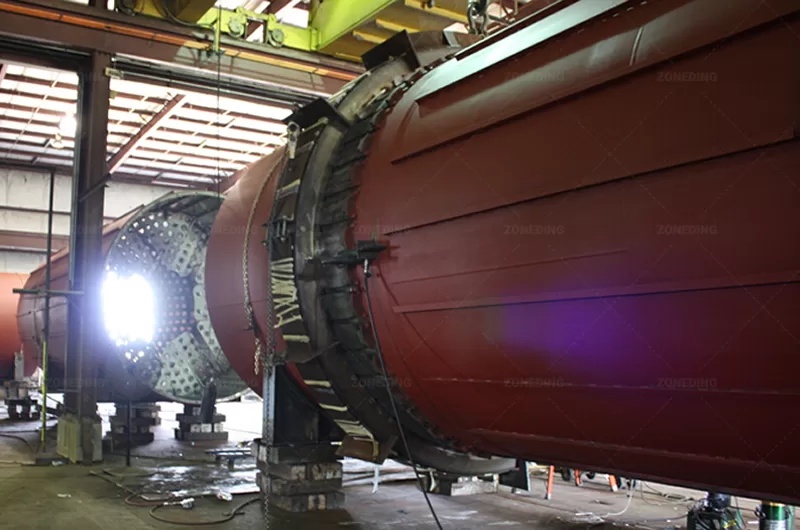



ZONEDINGMACHINE with demonstrated expertise in handling challenging materials like cassava residue and a strong commitment to after-sales support provides peace of mind and ensures better long-term operational success.
| Spec./m (Dia.×Length) | Shell Cubage (m³) | Capacity (t/h) | Installation Obliquity(%) | Highest Inlet Air Temperature(℃) | Main Motor (kw) | Weight (t) |
| Φ1.2×8.0 | 9.0 | 1.9~2.4 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 7.5 | 9 |
| Φ1.2×10 | 11.3 | 2.4~3.0 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 7.5 | 11 |
| Φ1.5×12 | 21.2 | 4.5~5.7 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 15 | 18.5 |
| Φ1.5×14 | 24.7 | 5.3~6.6 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 15 | 19.7 |
| Φ1.5×15 | 26.5 | 5.7~7.1 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 15 | 20.5 |
| Φ1.8×12 | 30.5 | 6.5~8.1 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 18.5 | 21.5 |
| Φ1.8×14 | 35.6 | 7.6~9.5 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 18.5 | 23 |
| Φ2.2×12 | 45.6 | 9.7~12.2 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 22 | 33.5 |
| Φ2.2×14 | 53.2 | 11.4~14.2 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 22 | 36 |
| Φ2.2×16 | 60.8 | 13.0~16.2 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 22 | 38 |
| Φ2.4×14 | 63.3 | 13.5~16.9 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 37 | 45 |
| Φ2.4×18 | 81.4 | 17.4~21.7 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 37 | 49 |
| Φ2.4×20 | 90.4 | 19.3~24.1 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 45 | 54 |
| Φ2.4×22 | 99.5 | 21.2~26.5 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 45 | 58 |
| Φ2.6×24 | 127.4 | 27.2~34.0 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 55 | 73 |
| Φ3.0×20 | 141.3 | 30.1~37.7 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 75 | 85 |
| Φ3.0×25 | 176.6 | 37.7~47.1 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 75 | 95 |
| Φ3.2×25 | 201 | 42.9~53.6 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 90 | 110 |
| Φ3.6×28 | 285 | 60.8~76.0 | 3~5 | 700~800 | 160 | 135 |



