全站搜索
Search the entire website
Search the entire website
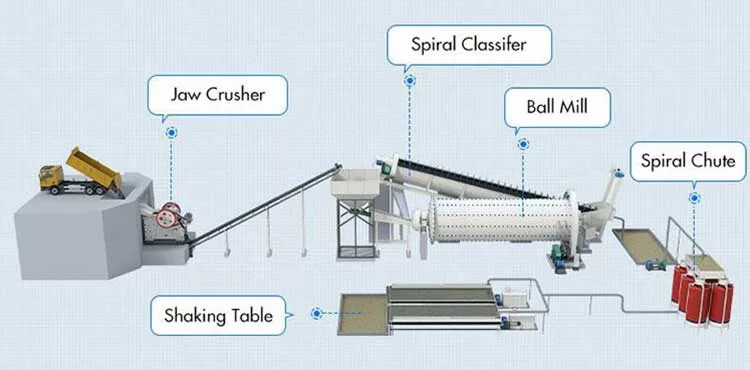
Spiral chute, which is also known as spiral chute separator, is a kind of gravity separation equipment.
Spiral gravity separator spiral chute is also called spiral concentrator or gravity separator, it’s a kind of gravity concentrator which can separate mineral particles according to density, granularity and shape by the interaction of centrifugal force, friction force of chute surface, water flow pressure and gravity of minerals. Spirals are made of high-density fiberglass, high quality emery and unsaturated resin.
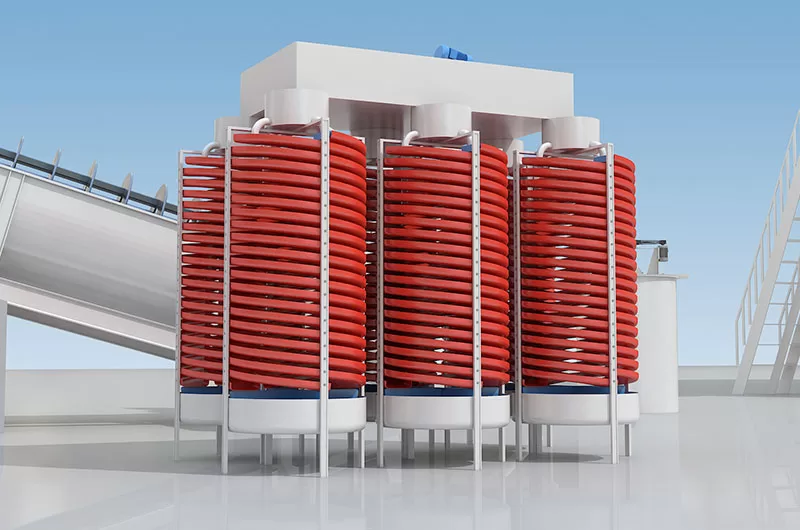
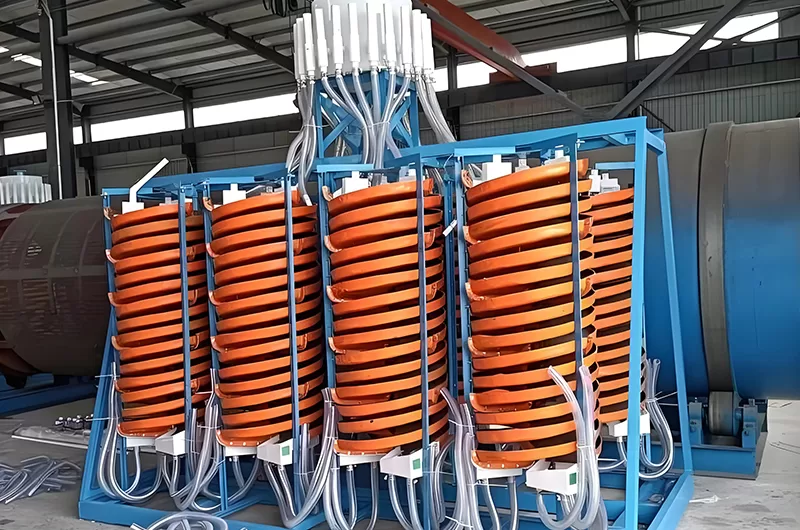


The spiral chute is suitable for separation of 0.3-0.02mm fine materials such as iron ore, ilmenite ore, chromite ore, pyrite ore, zircon ore, rutile ore, monazite ore, tungsten ore, tin ore, tantalum ore, niobium ore and other materials with enough specific gravity difference. It is the best roughing gravity equipment, which has been widely used in ferrous and nonferrous metal mines.

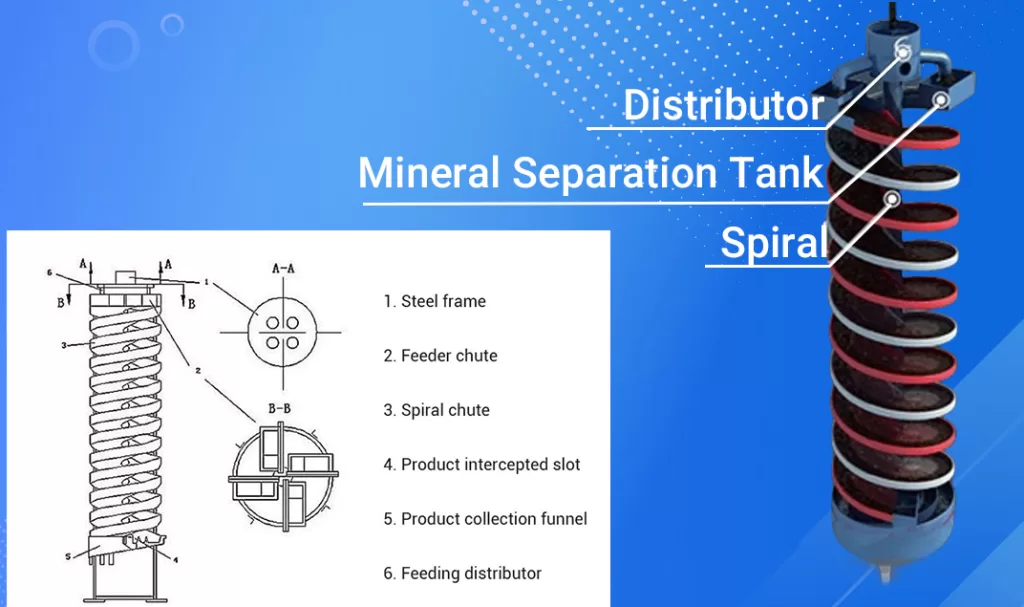
The spiral chute parts have a distributor and feed chute in the upper part and a product interceptor and collection chute in the lower part. The entire equipment is framed vertically with steel frames.The spiral chute is similar to the thread shape. The movement of the materials inside can be divided into three stages: the material introduction stage, the material acceleration stage, and the material uniform velocity warehouse stage. The third stage lasts the longest and is the key to materials crushing.
| Model | Processing capacity(t/h) |
| DL2000 | 15-40 |
| DL1500 | 8-16 |
| LL1200 | 4-6 |
| LL900 | 2-3 |



Answer: Key factors influencing separation include the table’s motion (stroke and frequency), water volume and slope, feed rate and concentration, and the feed material’s particle size and shape. Proper adjustment of these factors is critical for efficient separation. The table’s longitudinal and transverse slopes must be precisely controlled. The feed concentration should also be appropriate, typically 20-30% for coarse minerals and 15-25% for fine minerals.
Answer: Operation involves observing the bed surface and adjusting the slope, water flow, and feed rate. Regular maintenance includes checking for loose parts, lubricating moving components, inspecting for wear, and cleaning the table surface. Preventative maintenance should be performed regularly, with intervals ranging from every month to once a year.
Answer: Common issues can include table shaking or choppy cuts, uneven material distribution, or poor separation. Troubleshooting may involve checking for loose bolts, damaged springs, or misalignment, adjusting belt tension, inspecting electrical components, and ensuring proper lubrication. If there’s unusual noise, identify the source and eliminate the problem.
Answer:
Advantages: Shaking tables offer high enrichment ratios, are relatively simple to operate, and produce visible separation zones, allowing for easy adjustment and monitoring. They are suitable for a wide range of particle sizes and densities.
Disadvantages: They typically have lower throughput capacity compared to some other methods like jigs or spirals. They also require a relatively large footprint and consume a significant amount of water.
Answer: The selection depends on the material being processed, the desired throughput, and the particle size range. Factors to consider include the deck area, stroke length, and riffle design. Consulting with a manufacturer or expert is recommended to determine the optimal configuration.
